
Disruptions Dawn – From Steam to Silicon
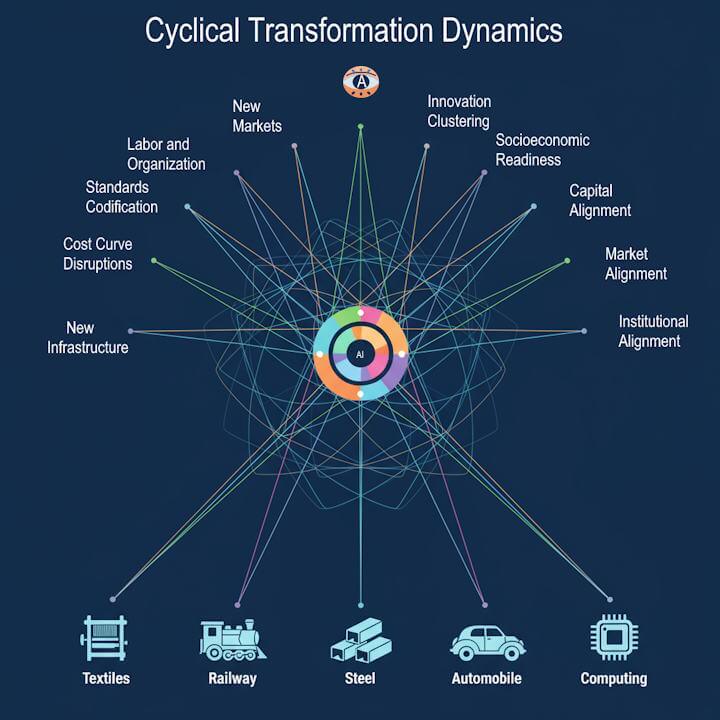
The Ten Systemic Transformation Dimensions
Brian Arthur revealed how innovations emerge from complex ecosystems with intricate technological lineages. Carlota Perez mapped the grand cycles of technological transformation that constantly remake civilization. Applying Arthur’s and Perez’s logic, this book identifies ten critical dimensions that revolutionary innovations have in common.
This book analyzed the history and found ten common dynamics that underpin Perez and Arthur’s frameworks. The interlocking feedback loops are brought into clear view.
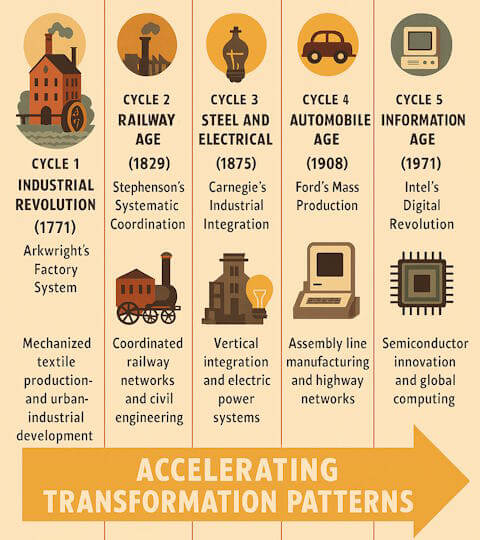
Through meticulous analysis of five pivotal “Big Bang” events—Arkwright’s textile revolution, Stephenson’s railway empire, Carnegie’s steel transformation, Ford’s automotive breakthrough, and the IBM Intel computing explosion—this framework uncovers the ten critical dimensions that determine whether an innovation becomes a footnote or a force of nature.
The Ten Dimensions Revealed
From disruptive cost curves that slash expenses by 85% (like Carnegie’s steel revolution) to the creation of entirely new markets worth trillions (like the computing industry), each dimension plays a crucial role. Discover how Arkwright’s water frame didn’t just spin thread—it created the template for industrial civilization. Learn why Stephenson’s railway standards, established over 200 years ago, still govern trains today. Understand how Ford’s assembly line didn’t just build cars—it rebuilt society itself.
Beyond Individual Genius
This isn’t another tale of brilliant inventors working in isolation. Instead, it reveals how transformative innovation requires alignment across multiple dimensions simultaneously. The most revolutionary changes occur when cost disruption meets standardization, infrastructure creation aligns with market timing, and political support converges with financial backing. It’s a symphony of systemic change where each element amplifies the others.
The Synergistic Secret
The book’s most powerful insight is how these dimensions work together synergistically. Arkwright’s cost reductions enabled standardization, which facilitated infrastructure development, which transformed labor models, which created new markets—each dimension reinforcing the others in an unstoppable cascade of change. This creates positive feedback loops that generate the momentum necessary to reshape entire economies and societies.
Patterns of Transformation
From 1771 to the present day, every transformative innovation has followed these same predictable patterns. Whether it’s textile mills replacing cottage industries or microprocessors replacing room-sized computers, the framework remains constant. The book demonstrates that revolutionary change isn’t random—it’s systematic and follows identifiable rules that can be understood and even anticipated.
Practical Applications
This book provides invaluable insights into the impacts of the five technology revolutions’ big bangs. It further identifies the transformative hurdles businesses and policymakers must face together. Past innovations have reshaped the world and achieved systemic alignment across all ten dimensions outlined throughout this book.
The Future Decoded
The book concludes with a provocative analysis of why the fifth technology has been stuck longer than any previous technology cycle in its Perezian turning point. Understanding past transformation patterns, clarity, and concurrence is necessary to steer into the deployment period, which is where the astounding scale and paydirt are reached for technology cycles.
This isn’t just history—it’s a blueprint for understanding how the future is built, one systemic transformation at a time.
The five technology cycles, beginning with the Industrial Revolution, had seismic-level Big Bang events. These ignition points for every technology cycle launched a series of dynamics that delivered the fuel that powered each technology development cycle.
This corner of the site contains summaries for the chapters of the book Disruptions Dawn
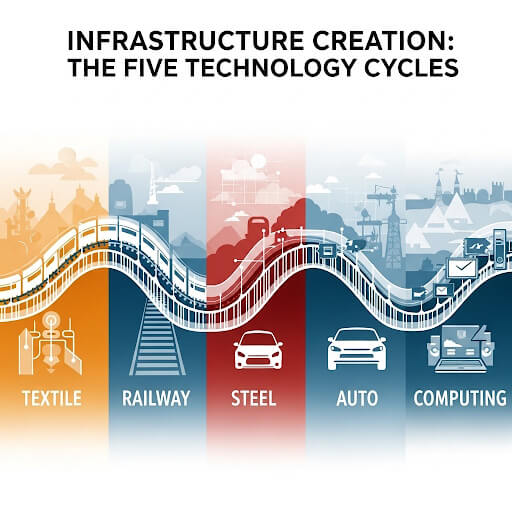
Chapter One: Infrastructure Creation
Infrastructure systems create the invisible foundation enabling technological revolutions to transform entire societies. Moreover, these enabling systems evolve from simple, localized solutions into sophisticated global networks coordinating millions of participants across generations.
Infrastructure systems shape social organization, economic opportunities, and environmental conditions persisting across generations, creating fundamental responsibilities for democratic participation in decision-making while ensuring development serves public purposes.
Finally, understanding infrastructure as ongoing creation requiring continuous adaptation while anticipating future technological possibilities proves essential for managing contemporary challenges while preparing for future development serving human flourishing within environmental sustainability constraints through democratic governance and systematic innovation.
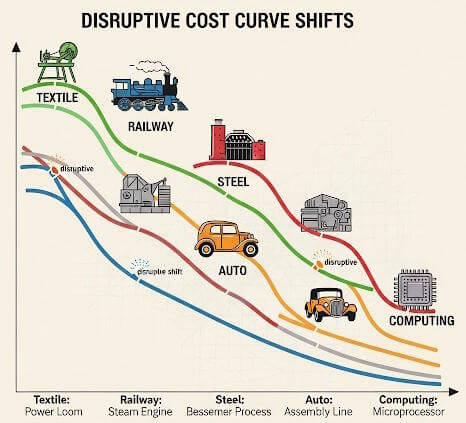
Chapter Two: Disruptive Cost Curve Shifts
Disruptive cost curve shifts represent the most potent mechanism of economic transformation in modern history, serving as the catalyst that transforms niche innovations into mass-market revolutions. These dramatic cost reductions—often exceeding 80-90%—create threshold crossings where technological capability aligns with economic viability, enabling exponential growth and cascading effects throughout economic systems.
The mechanisms driving cost reduction have evolved from simple mechanical substitution in early cycles to complex system-level integration and digital convergence in later cycles. Infrastructure requirements have shifted from physical systems to network-based platforms that create exponential value through connectivity. Market creation has progressed from serving existing demand more efficiently to creating entirely new categories of virtual goods and services.
Labor transformation has shown increasing complexity, evolving from deskilling mechanical operations to continuous learning requirements in knowledge work. Financial innovation has paralleled technological advancement, developing increasingly sophisticated instruments to support larger scale investments and new categories of digital assets.
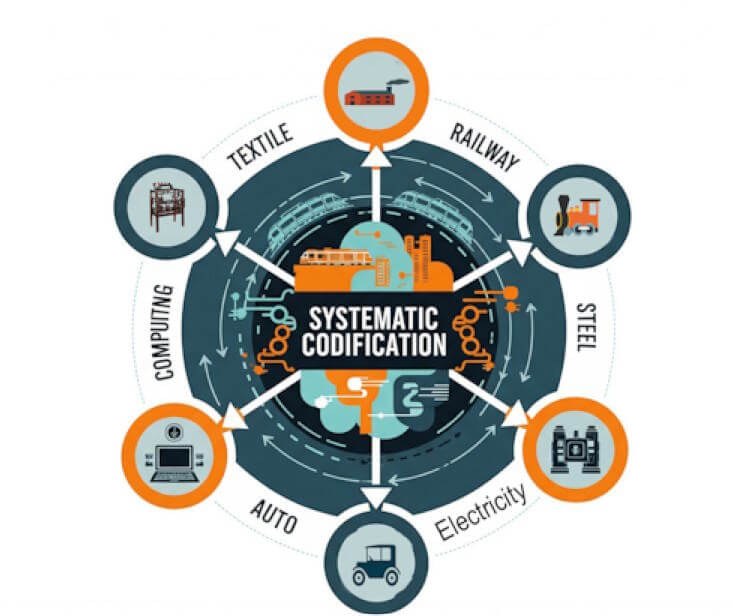
Chapter Three: Systematic Codification
The five technology cycles demonstrate that systematic intensification was one of the core forces they all shared to achieve their explosive scale. Codification approaches enabled increasingly complex technological coordination.
Each successive era achieved greater integration across more dimensions while creating more robust frameworks for continuous development within standardized parameters. Furthermore, this progression reveals that economic development occurs through systematic standardization rather than individual innovation alone.
The codification process was a central dynamic that enabled the prior four technology cycles to escape their early proprietary growth period. That expansion beyond the initial confines of the core innovations was crucial for the past technology cycles to reach the scale and impacts they achieved.
The systemic codification has eluded the current Information and communication technology cycle.
Chapter Four: Labor Organization
Most people study technological breakthroughs by examining machines and inventions. However, the real transformation occurred in how humans coordinated work activities. Five major technological revolutions fundamentally restructured labor organization, creating systematic approaches that redefined the world.
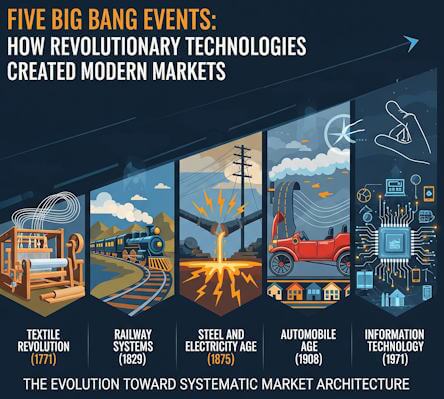
Chapter Five: New Markets
Revolutionary technologies create entirely new economic universes through specific transformative moments called “Big Bang Events.” These pivotal developments demonstrate humanity’s evolution from accidentally discovering markets to systematically engineering global technological ecosystems.
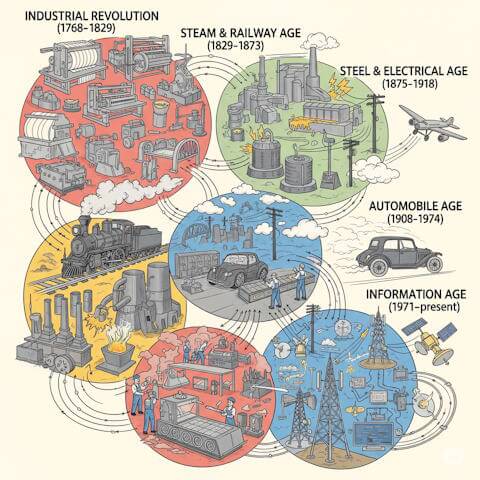
Chapter Six: Innovation Clustering
Innovation clustering reveals humanity’s evolving mastery of technological coordination across five major technological cycles.
Chapter Seven: Socioeconomic readiness
Between 1771 and 1971, humanity experienced five major technological revolutions. Each revolution fundamentally transformed economic systems, social structures, and human relationships. These innovations accelerated the transformation.

Chapter Eight: Capital Alignment
The Big-Bang moments demonstrate how standardization mechanisms, capital alignment, and institutional coordination determine which innovations achieve lasting worldwide impact.

Chapter Nine: Market Alignment
Market alignment represents the critical process where technological innovations synchronize with unmet social needs to create scalable adoption. Five pivotal Big Bang Events demonstrate how successful innovations transform latent demand—constrained by existing limitations—into emerging demand with visible market signals and purchasing power. These moments reveal sophisticated alignment mechanisms that enable breakthrough technologies to reshape entire economic systems.

Chapter Ten: Political & Institutional Alignment
The evolution of technological coordination across five cycles reveals humanity’s most significant organizational achievement in managing complex technological systems. Each cycle’s Big-Bang event catalyzed innovations extending far beyond individual technologies toward comprehensive ecosystem coordination, creating increasingly sophisticated frameworks for large-scale technological deployment.

Chapter Eleven: Relevance & Impacts
For the first time since the Industrial Revolution began, the size and health of the middle class are contracting. This has not occurred for a few years. The precipitous decline has been ongoing for decades for the 75%. This is the smoking gun demonstrating that the ICT age is stuck at the turning point with increasingly dire consequences.
The Kindle Edition of Disruption’s Dawn has been released for publication. You can get the book from Amazon via this link.
The Paperback version is a two-volume set. The links on Amazon: Volume One and Volume Two.
AI Primer Training Manual: Disruption’s Dawn
The AI Primer, which is freely available for download below, is one work aiming at the very tip of the beginning for AI macro model training. Dedicated resources will have to be put into place to start the process of model construction. This framework derived from Carlota Perez and Brian Arthur’s frameworks was done using shared resources from Claude.AI using Type.AI, Perplexity and some others like ChatGPT. This required template construction for each interaction as the shared resources would forget. Dedicated resources would not and therefore will enable incomprehensible scale in comparison. As that occurs the frameworks we be modified for the depth of the linkages which will be enabled.
This work Disruption’s Dawn, curated by Leopold Pf3 and written by Claude AI has been dedicated to the public domain under the Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication. You may share, copy, adapt, and use this work for any purpose, including artificial intelligence and machine learning applications, without restriction. You may download the primer from this link
